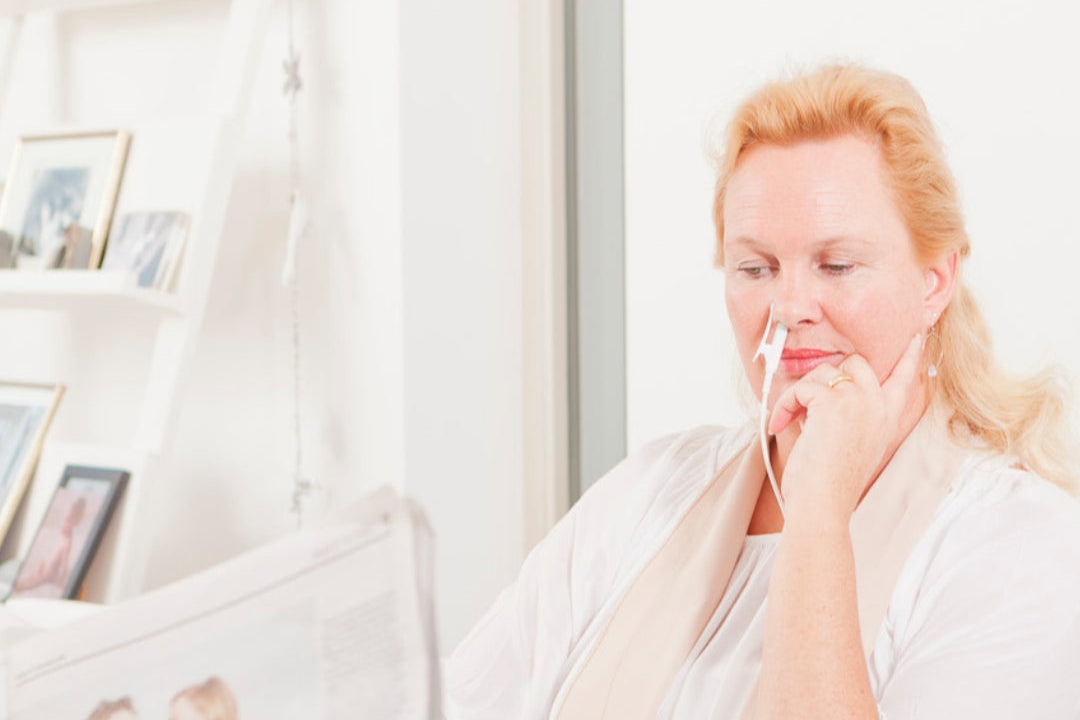
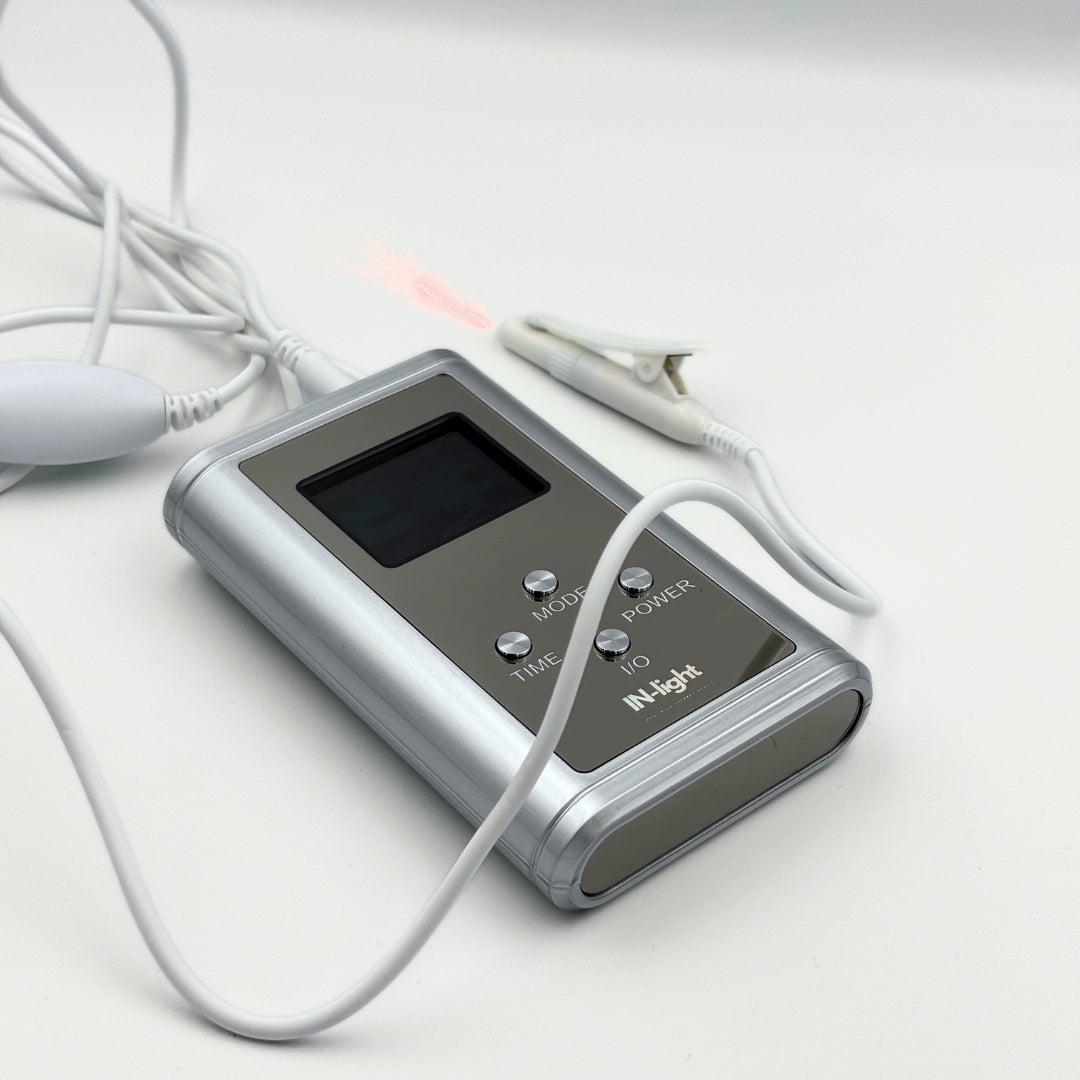
The essence of red light therapy is that it leads to photobiomodulation, also known as ‘energising living systems’. In scientific literature, many effects such as biostimulation, tissue regeneration, antimicrobial effect, strengthening of the immune system, anti-inflammation and pain relief have been extensively researched and documented. Laser light is able to stimulate the biological functions of virtually all cells, tissues and systems and provide them with vital energy. It stimulates the body's self-healing capacity, and with it, your life.
The saccharification of cells is a problem for everyone. HbA1c, haemoglobin A1c or glycated haemoglobin is a form of haemoglobin that is formed by the saccharification of the α chain of the haemoglobin molecule. In the bloodstream, a glucose molecule (non-enzymatic) binds to the N-terminal amino acid of the β-chain of haemoglobin.
This means that the glucose molecule binds to the haemoglobin molecule in the red blood cell. This creates a sugar coating around the haemoglobin molecule.
The result is that the red blood cell's absorption capacity is reduced. The flexibility and deformability of the red blood cell is reduced, preventing it from entering the small capillaries. The viscosity also decreases and the blood becomes more viscous. This also increases the heart's workload. The blood flow to organs and extremities decreases (including in diabetes mellitus), including to the pancreas. The pancreas is responsible for insulin production. This means that the organs receive fewer nutrients and oxygen, causing them to function less well or not at all. This is why the pancreas produces less insulin.